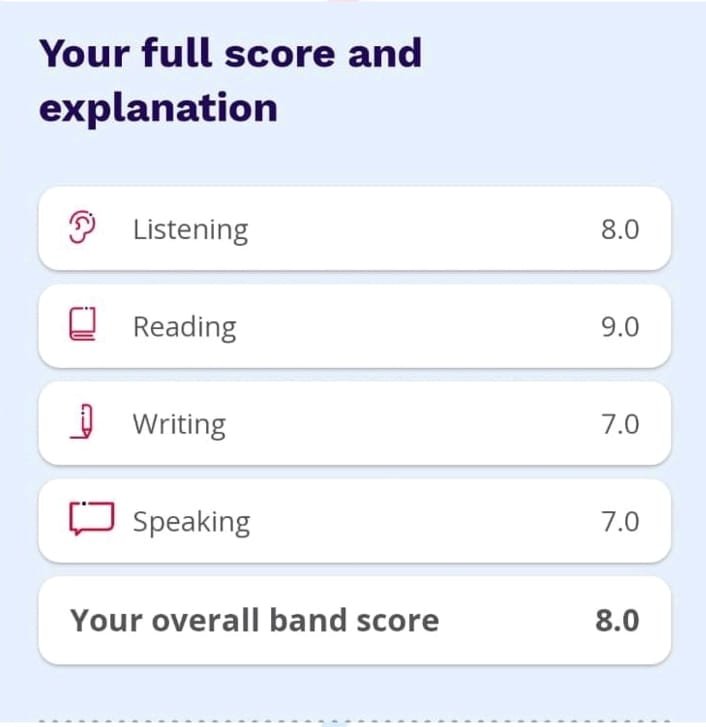
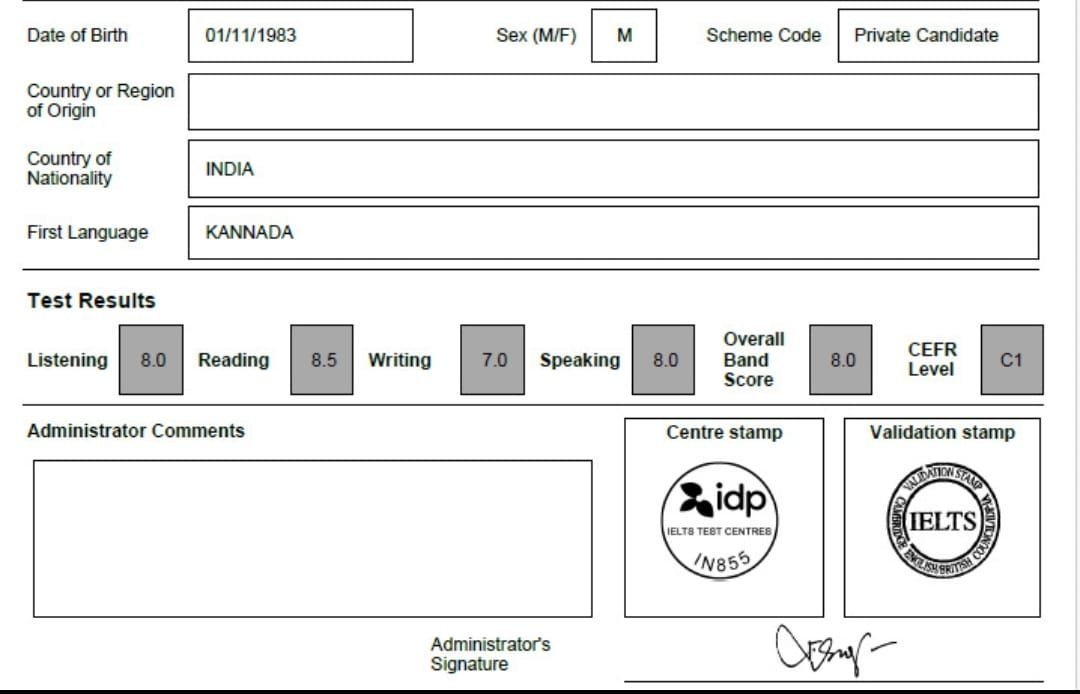
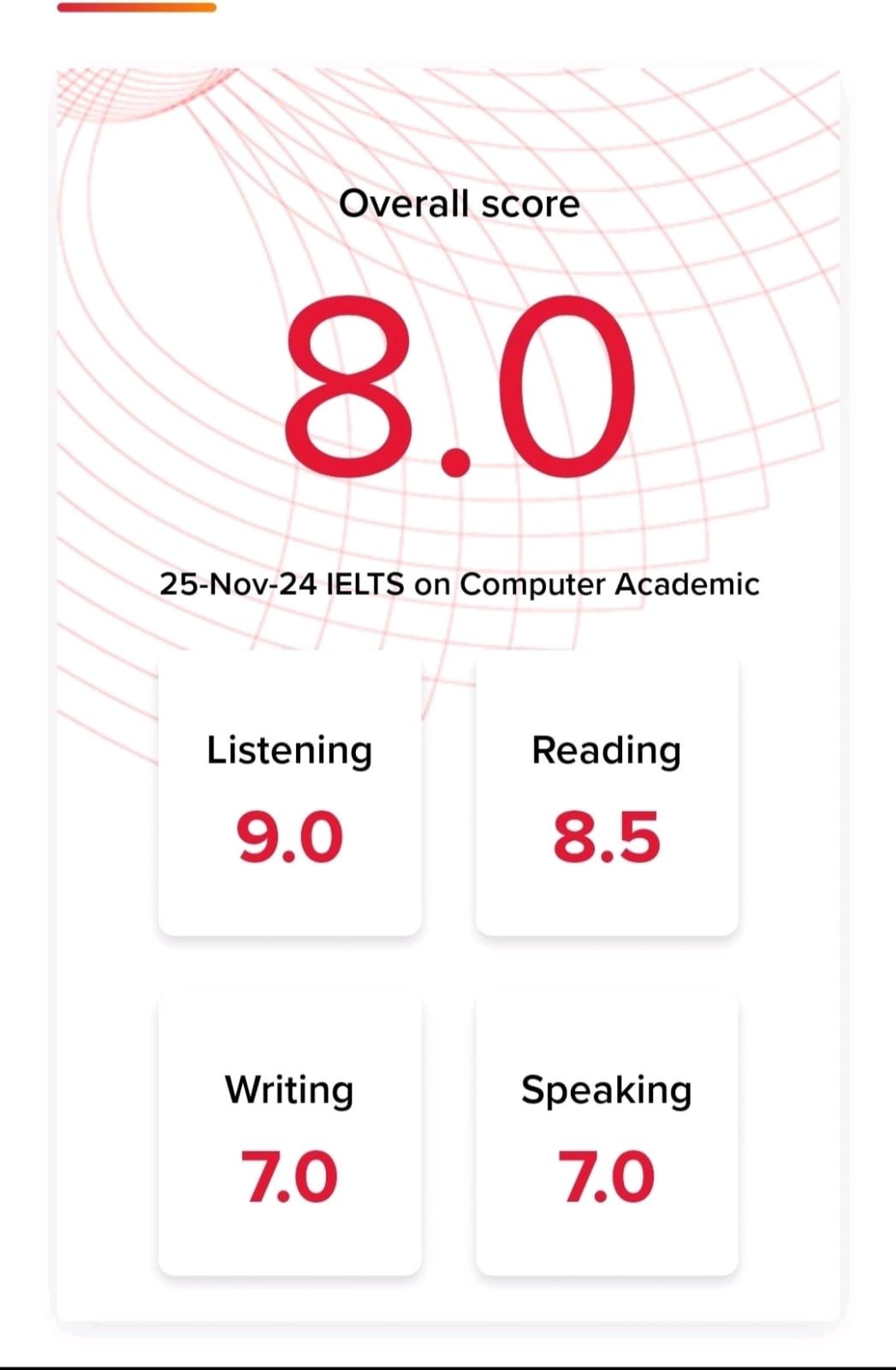
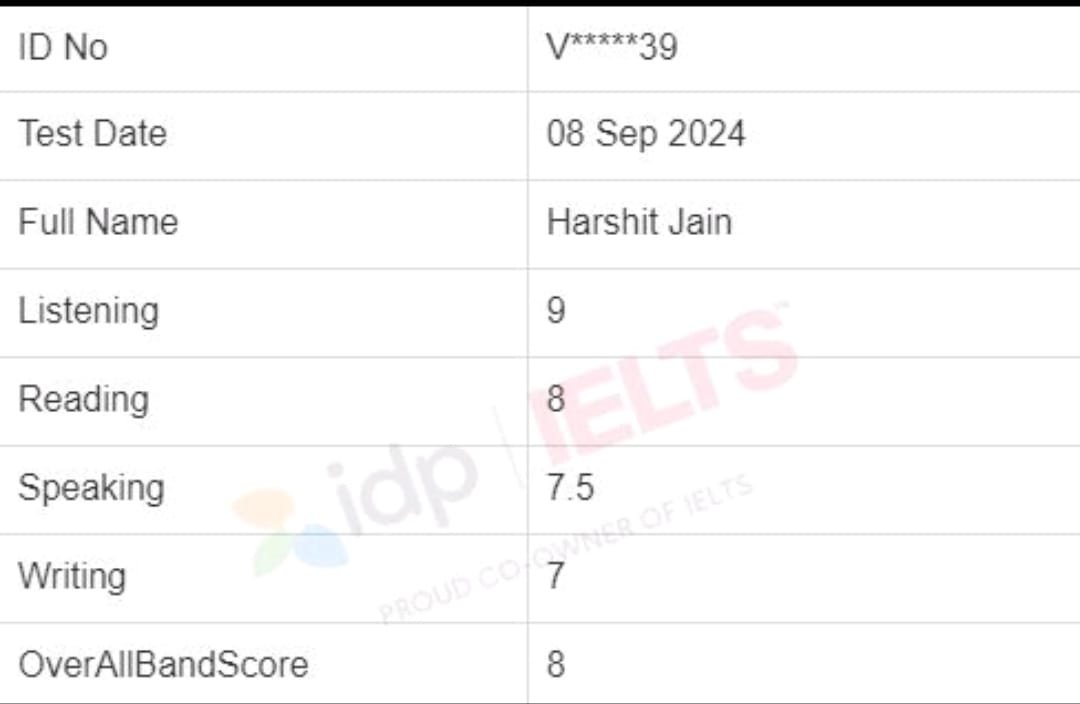
English is easy, we all will agree until the grammar mistakes are not shown! However, the grammar section of IELTS can be very tough. A list of the 20 most common grammar mistakes students make and how to avoid them, so that you can get your score up! Once you read, you will never feel grammar tough. Let’s start with me and find English grammar mistakes.
Table of Contents
1. Subject-Verb Agreement
- Mistake:- The books is on the table.
Correction:- The books are on the table.
(Plural subject “books” requires the plural verb “are.”) - Mistake:- She go to school every day.
Correction:- She goes to school every day.
(Singular subject “she” requires the singular verb “goes.”) - Mistake:– The team are playing well.
– Correction:- The team is playing well.
(Collective noun “team” is treated as singular in this context, so it requires the singular verb “is.”) - Mistake:- Everyone know the answer.
Correction:- Everyone knows the answer.
(Indefinite pronoun “everyone” is singular, so it requires the singular verb “knows.”) - Mistake:- The cats chases the ball.
Correction:- The cats chase the ball.
(Plural subject “cats” requires the plural verb “chase.”)
Tip: Ensure the subject and verb agree in number. For example, “He runs” (singular) vs. “They run” (plural).
2. Misuse of Articles
- Mistake: “She is the doctor.”
Correction: “She is a doctor.” (Use “a” for general professions unless referring to a specific one.) - Mistake: “We are going to a beach.”
Correction: “We are going to the beach.” (Use “the” when referring to a specific beach.) - Mistake: “I need an advice.”
Correction: “I need some advice.” (Articles are not used with uncountable nouns like “advice.”) - Mistake: “He is an best player on the team.”
Correction: “He is the best player on the team.” (Utilize “the” for superlatives like “best.”)
– Mistake: Wrong use of “a,” “an,” and “the.”
Tip: Use “a” before consonant sounds, “an” before vowel sounds, and “the” for specific nouns.
3. Incorrect Tense Usage
- Mistake: “Yesterday, I am going to the shop.”
Correction: “Yesterday, I went to the shop.” - Mistake: “He will graduate last year.”
Correction: “He graduated last year.” - Mistake: “I have seen her at the party last night.”
Correction: “I saw her at the party last night.” - Mistake: “She eats breakfast when I arrived.”
Correction: “She was eating breakfast when I arrived.”
– Common mistakes: Incorrect use of past, present, and future tenses.
Tip: Ensure tense consistency. If you start in the past tense, stick with it unless there’s a clear reason to shift tenses.
4. Run-On Sentences
- Mistake: “I love to travel I have been to many countries.”
Correction: “I love to travel, and I have been to many countries.” - Mistake: “She was tired she went to bed early.”
Correction: “She was tired, so she went to bed early.” - Mistake: “He studied for the exam he didn’t pass.”
Correction: “He studied for the exam, but he didn’t pass.” - Mistake: “The weather was cold we decided to stay inside.”
Correction: “The weather was cold; we decided to stay inside.” - Mistake: “I cooked dinner the kids watched TV.”
– Correction: “I cooked dinner while the kids watched TV.”
Mistake: The multi-independent clause sentences need to have appropriate punctuation.
Tip: Separate independent clauses with periods, commas plus a conjunction or semicolons.
5. Sentence Fragments
- Mistake: “Although I tried hard.”
Correction: “Although I tried hard, I couldn’t complete the task.” - Mistake: “Running late for the meeting.”
Correction: “I was running late for the meeting.” - Mistake: “After the movie ended.”
Correction: “After the movie ended, we went out for dinner.” - Mistake: “Without any explanation.”
Correction: “He left without any explanation.” - Mistake: “When the sun sets.”
Correction: “When the sun sets, the sky turns orange.”
Mistake: Writing incomplete sentences that lack a subject or verb.
Tip: Ensure every sentence has at least one subject and one verb.
6. Misplaced Modifiers
- Mistake: “Running down the street, the car almost hit the boy.”
Correction: “The car almost hit the boy running down the street.” - Mistake:“She served sandwiches to the children on paper plates.”
Correction: “She served the children sandwiches on paper plates.” - Mistake: “Covered in chocolate, John enjoyed the dessert.”
Correction: “John enjoyed the dessert covered in chocolate.” - Mistake: “I nearly spent all my money on clothes.”
Correction: “I spent nearly all my money on clothes.” - Mistake: “Driving to work, a deer crossed the road in front of me.”
Correction: “While I was driving to work, a deer crossed the road in front of me.”
Mistake: Placing descriptive words too far from the words they modify.
Tip: Place modifiers close to the words they describe to avoid confusion.
7. Incorrect Use of Prepositions
- Mistake: “She is good in math.”
Correction: “She is good at math.” - Mistake: “I will meet you in Monday.”
– Correction: “I will meet you on Monday.” - Mistake: “He is interested for science.”
– Correction: “He is interested in science.” - Mistake: “They arrived to the airport late.”
– Correction: “They arrived at the airport late.” - Mistake: “She apologized of the mistake.”
Correction: “She apologized for the mistake.”
Mistake: Using the wrong prepositions in phrases.
Tip: Learn common prepositional phrases and practice using them correctly.
8. Overuse of Passive Voice
- Mistake: “The letter was written by me.”
Correction: “I wrote the letter.” - Mistake: “The project was completed by the team.”
Correction: “The team completed the project.” - Mistake: “The cake was baked by her for the party.”
Correction: “She baked the cake for the party.” - Mistake: “The results were analyzed by the researchers.”
Correction: “The researchers analyzed the results.” - Mistake: “The essay was submitted by the student yesterday.”
Correction: “The student submitted the essay yesterday.”
– Mistake: Using passive voice excessively, making sentences less direct.
Tip: Use active voice where possible to make your writing clearer and more engaging.
9. Incorrect Plural Forms
- Mistake: “Sheeps are grazing in the field.”
Correction: “Sheep are grazing in the field.”
Tip: “Sheep” is an irregular noun and has the same form in both singular and plural. - Mistake: “I saw two mouses in the kitchen.”
Correction: “I saw two mice in the kitchen.”
Tip: The plural of “mouse” is “mice,” not “mouses.” - Mistake: “The childs are playing outside.”
Correction: “The children are playing outside.”
Tip: “Child” has an irregular plural form: “children.” - Mistake: “The informations are useful.”
Correction: “The information is useful.”
Tip: “Information” is uncountable, so it has no plural form. - Mistake: “She bought two furnitures.”
– Correction: “She bought two pieces of furniture.”
Tip: “Furniture” is uncountable and doesn’t take a plural form; use “pieces of” instead.
– Mistake: Using incorrect plural forms of nouns.
Tip: Learn the correct plural forms, especially irregular nouns (e.g., “children” instead of “childs”).
10. Confusing Homophones
- Their vs. There
– Mistake: “Their going to the park.”
– Correction: “They’re going to the park.”
(Tip: “Their” shows possession, while “there” refers to a place.) - Your vs. You’re
– Mistake: “Your the best friend I have.”
– Correction: “You’re the best friend I have.”
(Tip: “Your” is possessive, while “you’re” means “you are.”) - It’s vs. Its
– Mistake: “Its raining outside.”
– Correction: “It’s raining outside.”
(Tip: “It’s” means “it is,” and “its” shows possession.) - Then vs. Than
– Mistake: “She is taller then him.”
– Correction: “She is taller than him.”
(Tip: “Than” is used for comparisons, while “then” refers to time.) - To vs. Too
– Mistake: “I’m going too the store.”
– Correction: “I’m going to the store.”
(Tip: “Too” means “also” or “excessively,” while “to” is used for direction or purpose.)
Mistake: Mixing up words that sound the same but have different meanings (e.g., “their” vs. “there”).
11. Incorrect Use of Commas
- Incorrect: “After eating John went to the store.”
Correct: “After eating, John went to the store.” - Incorrect: “I bought apples oranges bananas and grapes.”
Correct: “I bought apples, oranges, bananas, and grapes.” - Incorrect: “She is smart funny and talented.”
Correct: “She is smart, funny, and talented.” - Incorrect: “Because it was raining we stayed inside.”
Correct: “Because it was raining, we stayed inside.” - Incorrect: “The dog barked but no one heard it.”
Correct: “The dog barked, but no one heard it.”
Mistake: Misplacing commas or omitting them where necessary.
Tip: Learn the rules for comma usage, such as after introductory phrases and in lists.
12. Lack of Parallel Structure
- Mistake: “She enjoys reading, to swim, and hiking.”
Correction: “She enjoys reading, swimming, and hiking.” - Mistake: “The job requires attention to detail, being organized, and you must work quickly.”
Correction: “The job requires attention to detail, organization, and quick work.” - Mistake:“He wanted to improve his speaking skills, listening to podcasts, and writing essays.”
Correction: “He wanted to improve his speaking skills, listen to podcasts, and write essays.” - Mistake:“In her free time, she likes to dance, cooking, and to paint.”
Correction: “In her free time, she likes dancing, cooking, and painting.” - Mistake:“The teacher was strict, patient, and has experience.”
Correction: “The teacher was strict, patient, and experienced.”
– Mistake: Failing to use the same grammatical structure in a list or comparison.
– Tip: Ensure elements in a series or comparison follow the same grammatical form.
13. Incorrect Pronoun Reference
- Mistake: “When John met Mark, he told him to be on time.”
Correction: “When John met Mark, John told Mark to be on time.”
(It is unclear who “he” and “him” refer to.) - Mistake: “The teacher gave the student her notes, but she couldn’t understand them.”
Correction: “The teacher gave the student her notes, but the student couldn’t understand them.”
(The pronoun “she” is ambiguous.) - Mistake: “If the employee doesn’t improve their performance, they will be let go.”
Correction: “If the employee doesn’t improve his or her performance, he or she will be let go.”
(The pronoun “their” is incorrect as it does not match the singular noun “employee.”) - Mistake: “I bought the cake for my sister, but she didn’t like it, which made me sad.
Correction: “I bought the cake for my sister, but she didn’t like the cake, which made me sad.”
(The pronoun “it” can cause confusion as to what “it” refers to.) - Mistake: “My mother told my aunt that she needs to cook dinner.”
Correction: “My mother told my aunt that my aunt needs to cook dinner.”
(It is unclear who “she” refers to—mother or aunt.)
– Mistake: Using pronouns that do not clearly refer to a specific noun.
Tip: Make sure every pronoun has a clear antecedent.
14. Double Negatives
- Mistake: “I don’t need no help.”
Correction: “I don’t need any help.” - Mistake: “She doesn’t know nothing about the test.”
Correction: “She doesn’t know anything about the test.” - Mistake: “He can’t never arrive on time.”
Correction: “He can never arrive on time.” - Mistake: “We haven’t seen nobody all day.”
Correction: “We haven’t seen anybody all day.” - Mistake: “They didn’t give us no information.”
Correction: “They didn’t give us any information.”
– Mistake: Using two negatives in a sentence, which creates a positive meaning.
Tip: Avoid double negatives; use a single negative to convey the intended meaning.
15. Incorrect Use of Conjunctions
- Mistake: “I wanted to go to the park but it was raining, however I went.”
Correction: “I wanted to go to the park, but it was raining, so I didn’t go.” - Mistake: “Neither she likes coffee nor tea.”
Correction: “She likes neither coffee nor tea.” - Mistake: “I studied hard because I did not pass the exam.”
Correction: “I studied hard because I wanted to pass the exam.” - Mistake: “Although it was late, but we continued working.”
Correction: “Although it was late, we continued working.” - Mistake: “I will go to the party if or unless you come with me.”
Correction: “I will go to the party if you come with me.” or “I won’t go to the party unless you come with me.”
– Mistake: Using the wrong conjunctions to connect ideas.
Tip: Learn the correct usage of coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions.
16. Incorrect Word Order
- Incorrect: Quickly the dog ran across the park.
Correct: The dog quickly ran across the park. - Incorrect: She to the store goes every day.
Correct: She goes to the store every day. - Incorrect: Yesterday I to my friend talked.
Correct: Yesterday I talked to my friend. - Incorrect: He bought for his sister a gift.
Correct: He bought a gift for his sister. - Incorrect: The movie I watched was interesting last night.
Correct: I watched an interesting movie last night.
– Mistake: Placing words in an order that makes the sentence unclear.
Tip: Follow standard English word order: subject + verb + object.
17. Incorrect Use of Apostrophes
- Incorrect: The company’s are launching new product’s next week.
Correct: The companies are launching new products next week. - Incorrect: Its a beautiful day for a walk in the park.
Correct: It’s a beautiful day for a walk in the park. - Incorrect: The childrens toys were scattered all over the room.
Correct: The children’s toys were scattered all over the room. - Incorrect: We went to my friends house for dinner.
Correct: We went to my friend’s house for dinner. - Incorrect: She cant find her keys anywhere.
Correct: She can’t find her keys anywhere.
– Mistake: Misplacing apostrophes in possessives and contractions.
Tip: Use apostrophes to show possession (e.g., “John’s book”) and in contractions (e.g., “don’t”).
18. Redundant Words
- Mistake: He made a brief summary of the report.
Correction: He made a summary of the report. - Mistake: She gave her final conclusion after the meeting.
Correction: She gave her conclusion after the meeting. - Mistake: Let’s meet at 10 AM in the morning.
Correction: Let’s meet at 10 AM. - Mistake: The end result was quite surprising.
Correction: The result was quite surprising. - Mistake: The store is offering a free gift with every purchase.
Correction: The store is offering a gift with every purchase.
– Mistake: Using unnecessary words that do not add meaning.
Tip: Be concise and eliminate redundant words from your writing.
19. Incorrect Use of Adjectives and Adverbs
- Incorrect: She sings beautiful.
Correct: She sings beautifully.
(“Beautiful” is an adjective; it should be “beautifully” to modify the verb “sings.”) - Incorrect: He runs quick.
Correct: He runs quickly.
(“Quick” is an adjective; it should be “quickly” to modify the verb “runs.”) - Incorrect: The cake smells deliciously.
Correct: The cake smells delicious.
(“Delicious” is an adjective; it modifies the noun “cake,” not the verb “smells.”) - Incorrect: She was real happy with her gift.
Correct: She was really happy with her gift.
(“Real” is an adjective; it should be “really” to modify the adjective “happy.”) - Incorrect: He completed the task careful.
Correct: He completed the task carefully.
(“Careful” is an adjective; it should be “carefully” to modify the verb “completed.”)
– Mistake: Confusing adjectives with adverbs.
Tip: Use adjectives to modify nouns and adverbs to modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
20. Incorrect Use of Countable and Uncountable Nouns
- Mistake: “She gave me a lot of advices.”
Correction: “She gave me a lot of advice.”
(Advice is uncountable, so it doesn’t take an “s.”) - Mistake: “There are less people in the room than yesterday.”
Correction: “There are fewer people in the room than yesterday.”
(People are countable, so “fewer” should be used instead of “less.”) - Mistake: “I don’t have many money left.”
Correction: “I don’t have much money left.”
(Money is uncountable, so “much” is the correct quantifier.) - Mistake: “He ate fewer rice than me.”
Correction: “He ate less rice than me.”
(Rice is uncountable, so “less” should be used instead of “fewer.”)
– Mistake: The wrong quantifiers with countable and uncountable statements.
Tip: Learn countable and uncountable nouns with quantifiers (e.g., many/countable nouns few) vs. much/uncountable upfront.
You can avoid these basic grammar mistakes by knowing what they are and practicing them often so your IELTS score is less likely to suffer unnecessarily.
Golden Tip:
Write essays and speak on general IELTS related topics to enhance your English grammar. Find grammar mistakes and fix them in specific grammar exercises. If you practice often enough, then there is a good chance that you can avoid these mistakes and improve your IELTS score!
Self-study Challenging? Overcome IELTS Challenges with Personalized Coaching
Your Local IELTS coach can assist if you are struggling with self-preparation. Whether you face challenges when it comes to time management, the complexities of IELTS concepts and techniques, or maintaining motivation, personalized coaching can add value in every single case. Instead of doing it all alone, you will get personal strategies and the right feedback to improve from your dedicated IELTS coach. If you feel self-study headaches then let me help you pass your IELTS test in the right direction.